LLM Visualization: How embedding space creates intelligence
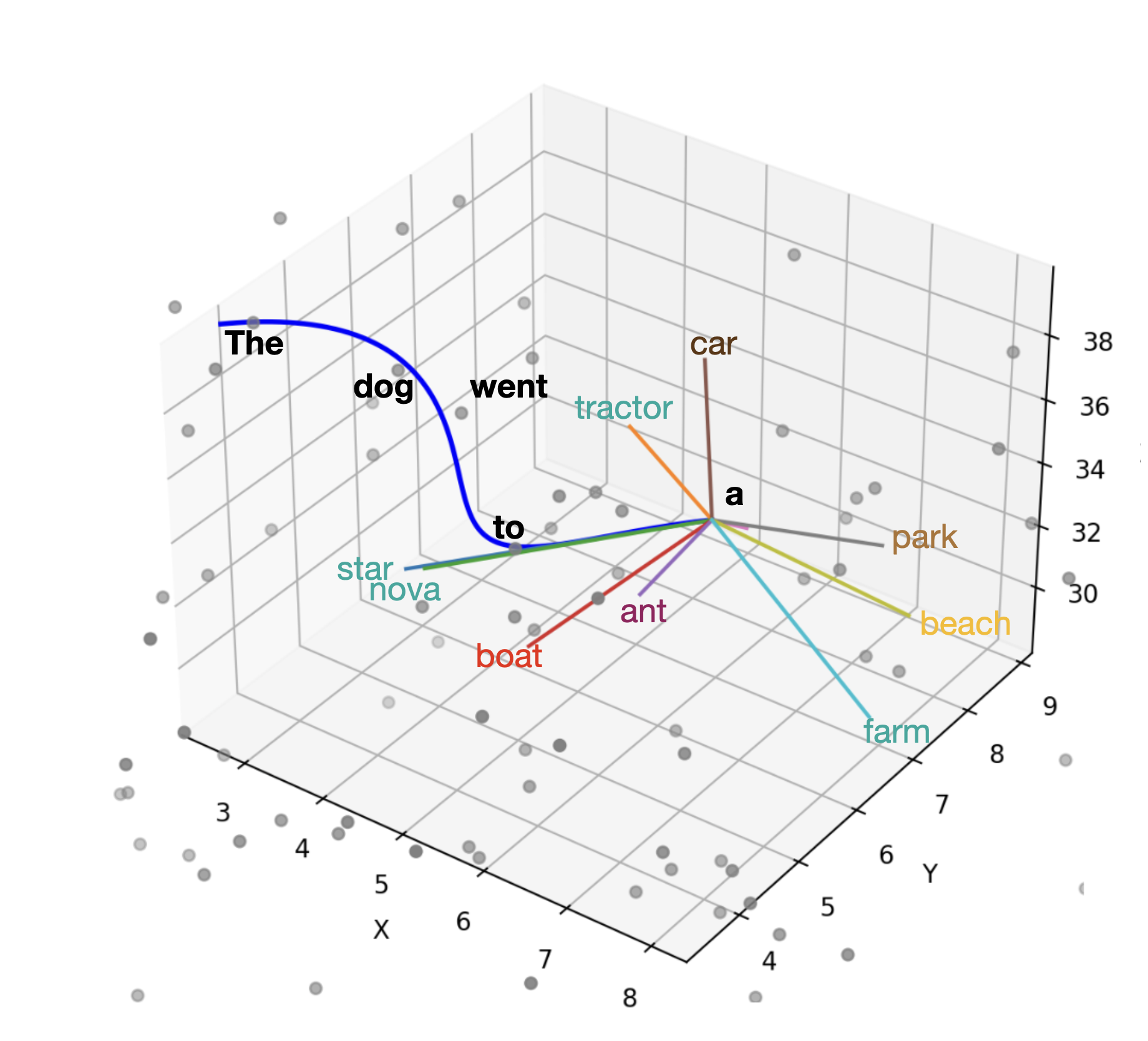
Using Python I created this visualization to help explain how LLMs capture and synthesize information. LLMs take the encoding of language and deconstruct it into concepts.
Multimodal LLMs take sound/images and map them to the concept spaces.
Then when you prompt a model with a question, the prompt establishes a “road” in a region of space that maps to related concepts, and the AI just continues on the most sensible path from this road to respond to the prompt.
The road, rather than being in 3 dimensions, is in thousands of dimensions, and this is what makes AI seem intelligent. The road can also be very winding and serpentine, it doesn’t have to be a straight line, and rarely is when you consider that an LLM can have 3 thousand dimensions or more that it’s carving a path through.
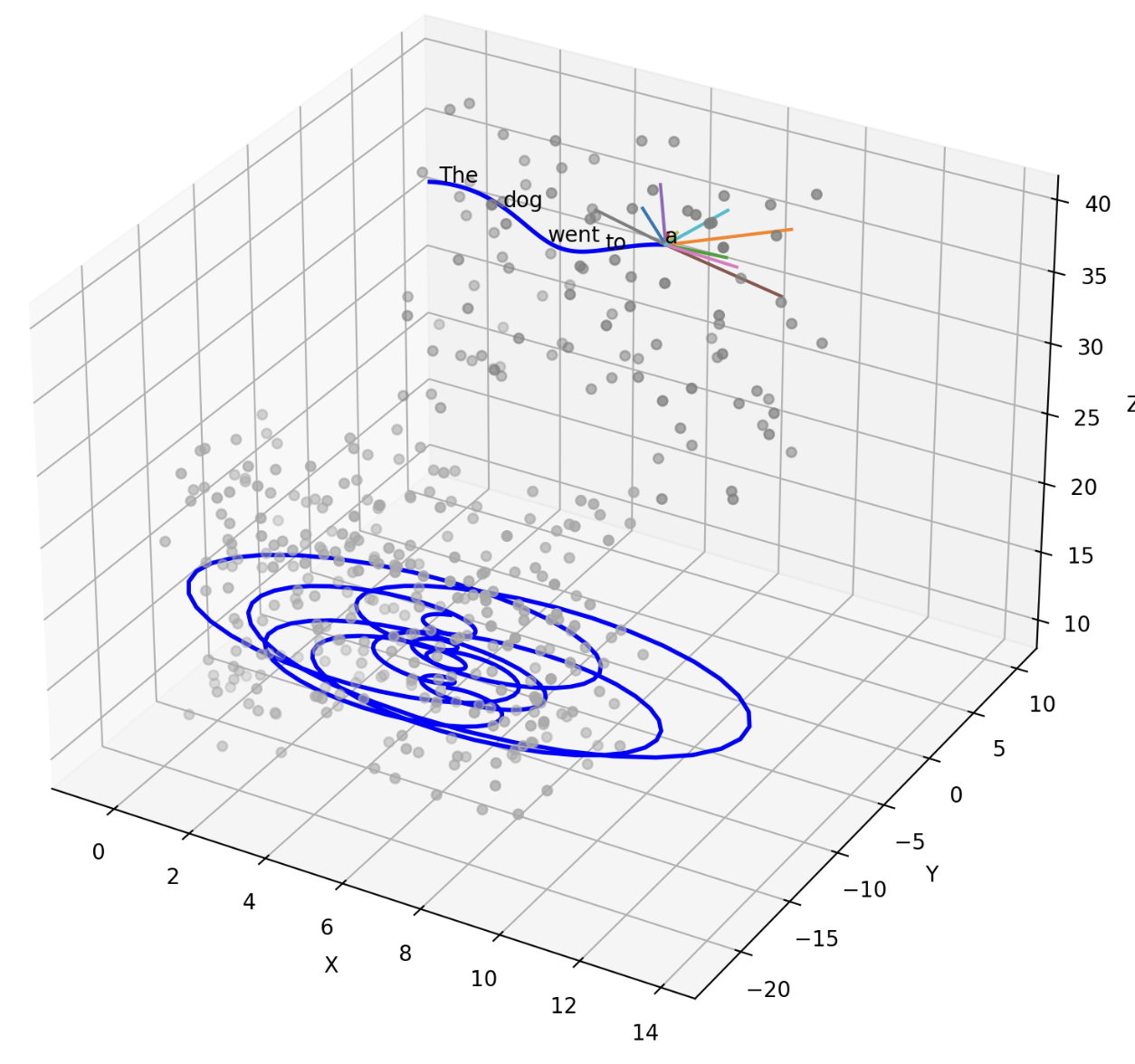 Image Caption: A comparison of a smooth path and a spirally winding path.
Image Caption: A comparison of a smooth path and a spirally winding path.
For some additional reading on the topic, I recommend the following articles:
- Moebio live interactive visualization of a latent space and how it connects to a text prompt. By far the best visualization I’ve seen of this concept. (note page may take a minute or so to load)
- Galileo This is an embedding space viewer and clustering tool that can be used to visualize the concept space of an LLM
- LatentScope Another tool for visualizing an embedding space
Note that any tool to turn a thousand dimensional space to 2D or 3D will always be a lossy representation
 Want to work with me? Send me an email.
Want to work with me? Send me an email.